Azerbaijan's BRICS bid, Georgia's Western orientation, Armenia's military enhancements Political summer in Caucasus
The summer of 2024 saw pivotal political shifts in the South Caucasus, profoundly influencing both regional and global dynamics. Below are the key highlights from a security perspective.
Baku's future priorities
Azerbaijan has notably enhanced its position within the global political landscape, underscoring its multi-vector foreign policy approach.
Firstly, Azerbaijan has officially applied for membership in BRICS, and it has garnered support from several member states of the organization. President Ilham Aliyev has been invited to attend the BRICS summit scheduled to take place in Kazan this October.
BRICS, an intergovernmental coalition, currently includes Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa, Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran, and the United Arab Emirates.

The benefits of BRICS membership for Azerbaijan include strengthening political and economic relationships with member countries of the Global South. Additionally, joining BRICS would allow Azerbaijan to diversify its foreign economic relations and establish new trade partnerships, potentially expanding markets for its domestic products.
Another important aspect is that Azerbaijan's participation in BRICS carries no significant risks or threats. As a member of the Non-Aligned Movement and not part of any military alliance, Azerbaijan's involvement in BRICS—an organization without binding obligations or restrictions—fits well within its strategic framework.
Secondly, Azerbaijan has bolstered its relations with Uzbekistan by signing a treaty of alliance. On August 23, during a state visit to Tashkent, the leaders of both nations signed the "Treaty on Allied Relations between the Republic of Azerbaijan and the Republic of Uzbekistan" and adopted the "Decision of the First Meeting of the High Intergovernmental Council of the Republic of Azerbaijan and the Republic of Uzbekistan."
This strengthening of the strategic alliance between the two countries is a significant development for the Turkic world, especially in the context of the shifting global order.
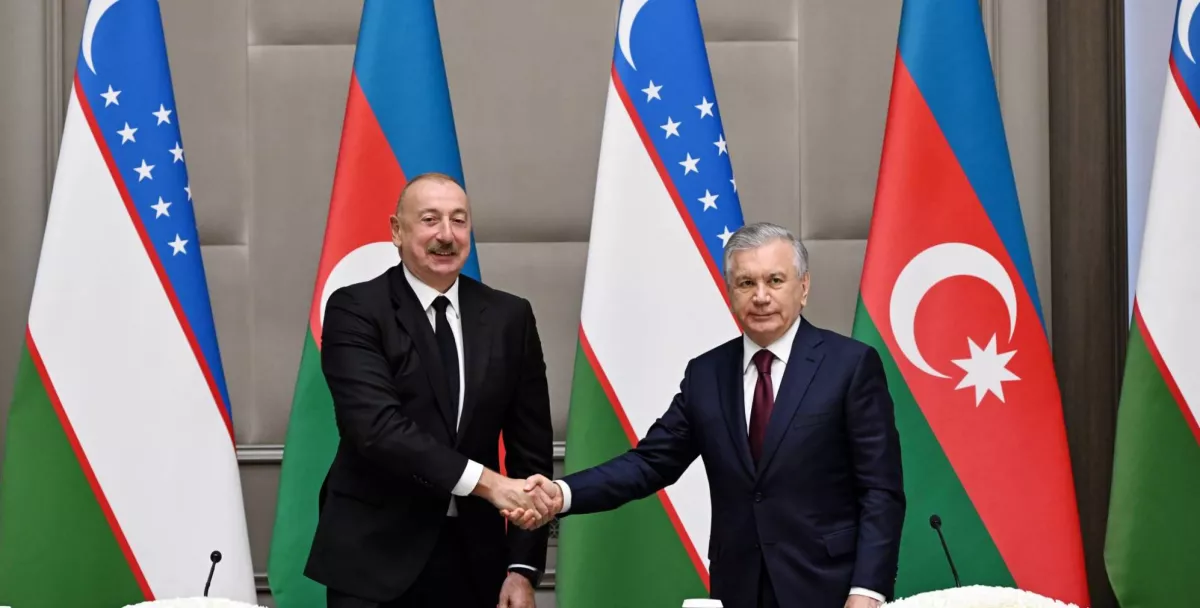

Thirdly, President Vladimir Putin's state visit to Baku underscored that strengthening relations with Russia remains a central element of Azerbaijan's foreign policy. By maintaining robust political dialogue and expanding trade, economic, and other ties with Russia, Azerbaijan effectively balances its relations with Ukraine and Western nations. This nuanced strategy enables Azerbaijan to project itself as an independent player in both global and regional politics, prioritizing its national interests over alignment with major world powers.

Fourthly, Baku is actively advancing the peace agenda with Armenia, aiming for a comprehensive agreement. In July, President Ilham Aliyev announced at an international media forum in Shusha that 80 per cent of the peace agreement's text had been finalized. He outlined two critical conditions: Azerbaijan expects Yerevan to take definitive action regarding the dissolution of the OSCE Minsk Group and amend the Armenian Constitution, which currently retains territorial claims against Azerbaijan. The president's remarks send a clear message to Yerevan that these issues must be addressed for a peace agreement to be achieved.
Georgia: Defending itself while staying Western
Georgia's political landscape this summer has been notably turbulent. The enactment of the foreign agents law caused a strain in relations with the US and the EU, a trend that persisted throughout the summer.
Specifically, the US imposed visa sanctions on numerous Georgian officials, including members of parliament and government officials involved in the law's adoption. Concurrently, the European Union began considering sanctions against Georgia, with Estonia, the Netherlands, the Czech Republic, and Sweden being particularly proactive, according to reports from the Financial Times.
Despite the deterioration in relations with the West, Georgia has maintained its foreign policy orientation. Prime Minister Irakli Kobakhidze confirmed that the amendments to Article 78 of the Georgian Constitution, which express the country's commitment to joining the EU and NATO, will remain unchanged.
This indicates that the Georgian government remains committed to its Euro-Atlantic aspirations and integration with the European Union. At the same time, Tbilisi continues to strengthen its trade and economic relationships with Russia, reflecting Georgia's stance as a sovereign state in the South Caucasus that prioritizes its national interests.
Armenia: Progress or regress?
In recent months, Armenia's domestic political scene has been marked by a series of subdued opposition protests aimed at altering the leadership in the "country of stones." Concurrently, Yerevan has been actively enhancing its military capabilities, acquiring modern offensive weaponry from France, the United States, and India, either through purchase or as part of agreements facilitated by Brussels. Armenia has emerged as a significant client for both public and private Indian defence firms. Recently, the country has received advanced French 155mm CAESAR self-propelled artillery systems, as well as anti-tank missile systems and air-to-air missiles, bolstering its military arsenal.
The Armenian military has recently bolstered its arsenal with an array of advanced weaponry. This includes dozens of R511 and R530 air-to-air missiles, 30 ERYX anti-tank missiles, and several German-made DM32 grenade launchers, commonly referred to as “bunkerfaust.”
Additionally, Armenia has received Panzerfaust 3 anti-tank systems, approximately 500 French-made APILAS disposable hand grenades, and 50 American BGM-71 TOW anti-tank missile systems. Furthermore, military cooperation between the US and Armenia has intensified, leading to the deployment of American military personnel and equipment in Zangazur.

The ongoing militarization of Armenia raises concerns about the potential for rapid normalization of relations between Armenia and Azerbaijan, particularly in light of enduring revanchist sentiments within Armenian society. However, there has been notable progress in the area of border delimitation between the two countries.
Baku and Yerevan have recently signed an agreement outlining the joint activities of their respective border delimitation commissions. This agreement, finalized under the protocol developed during the meeting on state border delimitation and border security on April 19, 2024, marks a significant step forward.
The next expected moves from Armenia include amending the Armenian Constitution to remove territorial claims against Azerbaijan and agreeing to the dissolution of the OSCE Minsk Group. Azerbaijan is anticipating these concrete actions from Yerevan.
Ultimately, it remains to be seen whether the Armenian leadership will exhibit the necessary political will to meet Azerbaijan's conditions and advance towards a comprehensive peace agreement.








